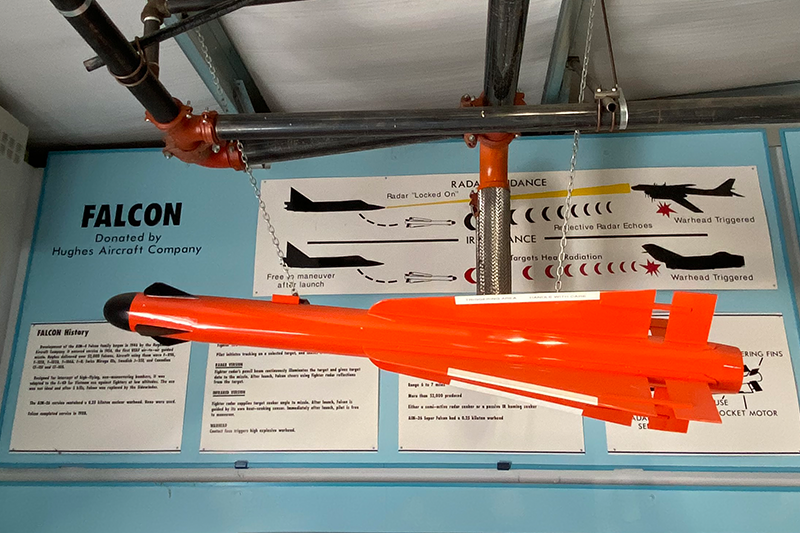
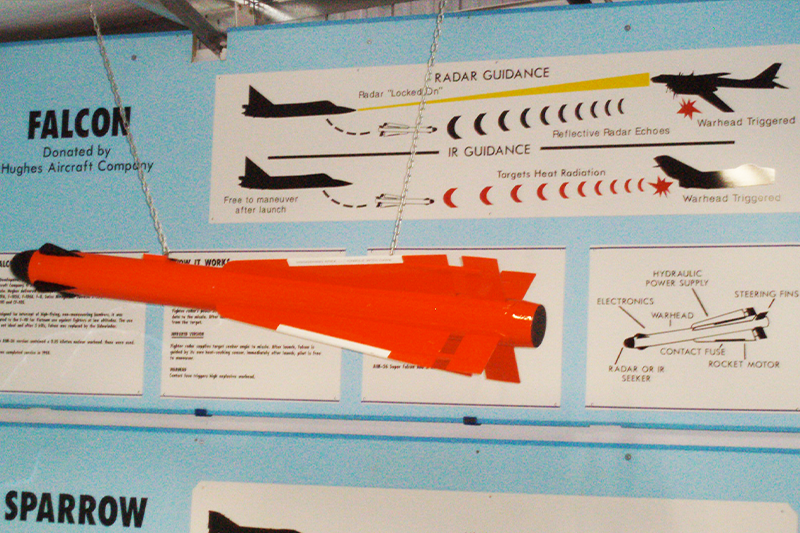
Specifications
Specifications
| Primary Function: | Target Drone | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function: | Guided short-range missile | |
| Powerplant: | Morton Thiokol M-46 | |
| Thrust: | 4,429 lb | |
| Speed: | 2,113 mph | |
| Range: | 5.6 nautical miles | |
| Length: | 7.22 feet | |
| Diameter: | 7.9 inches | |
| Wingspan: | 23.6 inches | |
| Warhead: | Blast fragmentation | |
| Guidance System: | Semi-actifve and active radar homing | |
| Aircraft Platforms: | F-4D, F-89, F-101, F-106, Mirage IIS J-35, JA-37 | |
| Unit Cost: | $386,000 | |
| Manufactured By: | Hughes Aircraft Company | |
History
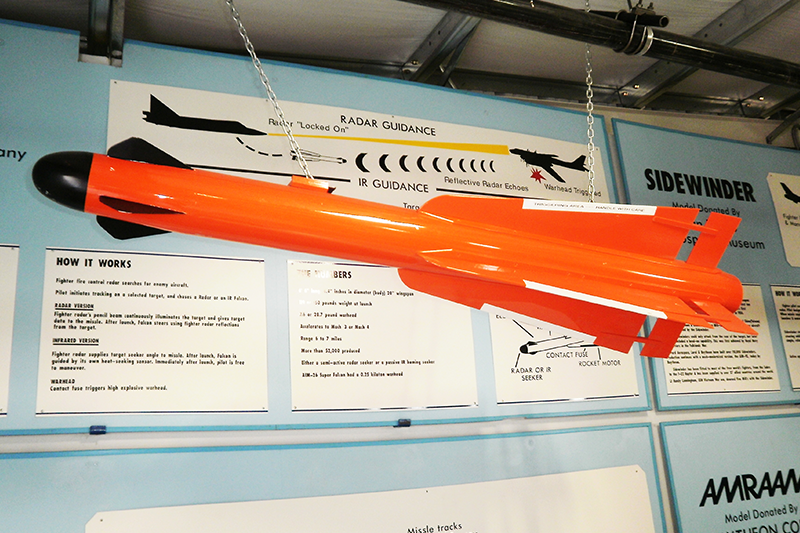
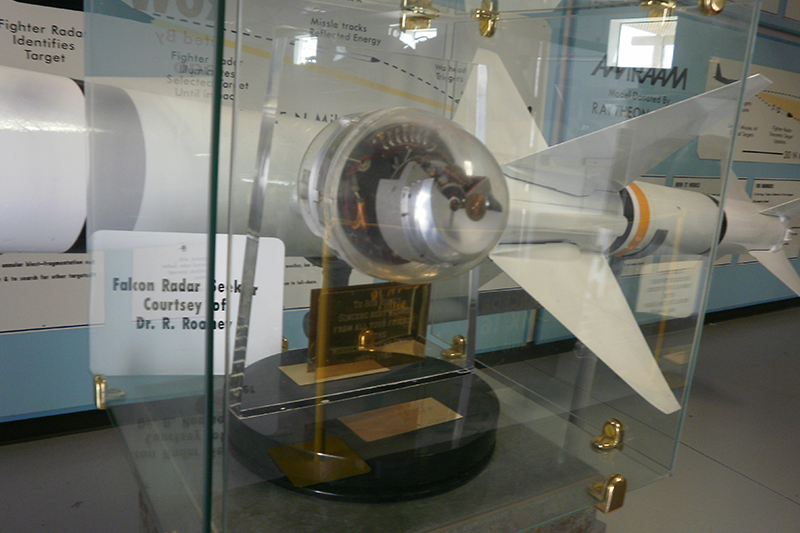
A product of Hughes under Project Dragonfly, the Falcon was first fielded in 1955, reaching inidial operational capability (IOC) sometime in mid-1956. It had long cord delta wings, separate rear fins and nose-mounted receiver antennae. These were often mistaken for canards, but control was by elevons on the trailing edges of the wings. The Falcon fitted either infrared (IR) or semi-active RADAR homing (SARH) seeker heads, and was propelled by a single-charge 6,000 lb. thrust Thiokol motor. It was capable of Mach 3 speeds over its six mile range, and over 41,000 of the A, B and C models were produced. The B Model included the improved seeker heads.
The missile could not be launched by the F-106 Delta Dart in most of its flight regimes, and in 1958 the Super Falcon entered service for this aircraft. This version had no forward antennae, but was longer, with bigger wings and fins, a more powerful warhead and longer burning motor. Only a few of these E versions were produced, the F and G versions with leading edge strakes and a two charge motor beginning production in 1959. The E retained the overall orange color scheme of the earlier models, but the F and G adopted a half red, half white pattern.
The AIM-4 was followed by the AIM-26 and AIM-47, also called Falcons, though they were entirely different missiles. Both were much larger and nuclear capable, though the AIM-47, intended for use with the F-108 Rapier and later the YF-12A Blackbird, never entered active service. The AIM-47 was white with black reticle stripes, and seven test firings were conducted from a YF-12A between March 1965 and September 1966, with six successful intercepts. The Phoenix is descended from this missile, and an air-to-ground derivative of the AIM-47 was briefly evaluated as the XAGM-76A.
The AIM-26A Nuclear Falcon was developed to provide a head-on kill capability against enemy bombers. It fitted the W-54 "Wee Gnat" warhead1 and was white overall with a black nose tip and RADAR receivers. To provide attack capability against low-flying targets over friendly territory, the conventionally armed AIM-26B was developed. Both were in active service from 1961 to 1971, and in 1980 the -26B was exported to the Swiss Air Force as the HM-55 and began production under license by SAAB as the Rb27.
Finally, in 1963 the AIM-4D was produced, combining the small airframe of the original Falcon with the more powerful motor, improved IR seeker and color scheme of the later Supers. Intended as an interim solution until better models of the Sidewinder became available, it is the only Falcon to be fired in anger. Used in Vietnam, it proved to be relatively ineffective due to its limited maneuverability, tendency to cause engine flameouts in the launching aircraft, small warhead, long launch time and lack of a proximity fuse. It did, however, manage to shoot down four MiG-17s and one MiG-21 between October 26, 1962 and February 5, 1968, though this was out of 54 missiles launched during Linebacker. A number of A and C models were converted to the D configuration, and the version was built under licence by SAAB as the Swedish Rb28, as well as being exported to the Swiss Air Force as the HM-58.
The AIM-4H with a proximity fuse and LASER homing was begun in 1969 but abandoned in 1971 without reaching service. All Falcons were withdrawn from active service in the US by 1988, but during its lifetime, the AIM-4 was fielded on the F-4D Phantom, F-89 Scorpion, F-101 Voodoo, F-102 Delta Dagger, F-106 Delta Dart, Dassault's Mirage IIIS, and SAAB's J-35 Draken and JA-37 Viggen. It was tested for possible use on the F-94 Starfire, and was to have armed the F-12A Blackbird, Republic F-103 and F-108 Rapier. It has served with the Air Forces of Japan, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Canada, Greece and others.